![[Previous]](../prev.gif) |
![[Contents]](../contents.gif) |
![[Index]](../keyword_index.gif) |
![[Next]](../next.gif) |
![[Previous]](../prev.gif) |
![[Contents]](../contents.gif) |
![[Index]](../keyword_index.gif) |
![[Next]](../next.gif) |
 |
This version of this document is no longer maintained. For the latest documentation, see http://www.qnx.com/developers/docs. |
Spawn a child process, given a vector of arguments, an environment, and a relative path
#include <spawn.h>
int spawnvpe( int mode,
const char * file,
char * const argv[],
char * const envp[] );
variable=value
that's used to define an environment variable.
libc
Use the -l c option to qcc to link against this library. This library is usually included automatically.
The spawnvpe() function creates and executes a new child process, named in file with the NULL-terminated list of arguments in the argv vector.
 |
If the new child process is a shell script, the first line must start with #!, followed by the path of the program to run to interpret the script, optionally followed by one argument. The script must also be marked as executable. For more information, see "The first line" in the Writing Shell Scripts chapter of the Neutrino User's Guide. |
The spawnvpe() function isn't a POSIX 1003.1 function, and isn't guaranteed to behave the same on all operating systems. It calls spawnp().
To view the documentation for a function, click its name in this diagram:
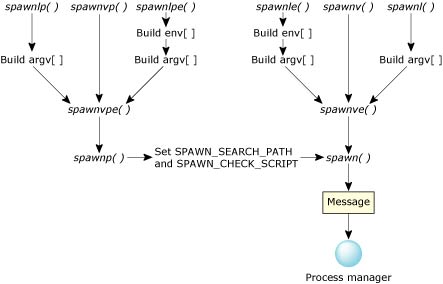
Most of the spawn*() functions do a lot of work before a message is sent to procnto.
If the value of envp is NULL, then the child process inherits the environment of the parent process. The new process can access its environment by using the environ global variable (found in <unistd.h>).
The following arguments are passed to the underlying call (spawnp()):
Create temporary attribute structure and set the flags member based on the mode:
 |
A parent/child relationship doesn't imply that the child process dies when the parent process dies. |
The spawnvpe() function's return value depends on the mode argument:
| mode | Return value |
|---|---|
| P_WAIT | The exit status of the child process. |
| P_NOWAIT | The process ID of the child process. To get the exit status for a P_NOWAIT process, you must use the waitpid() function, giving it this process ID. |
| P_NOWAITO | The process ID of the child process, or 0 if the process is being started on a remote node. You cannot get the exit status of a P_NOWAITO process. |
If an error occurs, -1 is returned (errno is set).
| Safety: | |
|---|---|
| Cancellation point | Read the Caveats |
| Interrupt handler | No |
| Signal handler | No |
| Thread | Yes |
If mode is P_WAIT, this function is a cancellation point.
execl(), execle(), execlp(), execlpe(), execv(), execve(), execvp(), execvpe(), getenv(), putenv(), setenv(), spawn(), spawnl(), spawnle(), spawnlp(), spawnlpe(), spawnp(), spawnv(), spawnve(), spawnvp(), wait(), waitpid()
Processes and Threads chapter of Getting Started with QNX Neutrino
![[Previous]](../prev.gif) |
![[Contents]](../contents.gif) |
![[Index]](../keyword_index.gif) |
![[Next]](../next.gif) |