Create and execute a new child process
#include <spawn.h>
pid_t spawn( const char * path,
int fd_count,
const int fd_map[ ],
const struct inheritance * inherit,
char * const argv[ ],
char * const envp[ ] );
- path
- The full path name of the executable.
- fd_count
- The number of entries in the fd_map array.
- fd_map
- An array of file descriptors that you want the child process to inherit.
If fd_count isn't 0, fd_map must contain
at least fd_count file descriptors, up to OPEN_MAX
FDs.
If fd_count is 0, fd_map is ignored.
If you set fdmap[X] to
SPAWN_FDCLOSED instead of to a
valid file descriptor, the file descriptor X is closed in the
child process.
If fd_count is 0, all file descriptors
(except for the ones modified with fcntl()'s
FD_CLOEXEC flag)
are inherited by the child process.
- inherit
- A structure, of type struct inheritance, that indicates
what you want the child process to inherit from the parent.
For more information, see
"inheritance structure,"
below.
- argv
- A pointer to an argument vector.
The value in argv[0] should represent the filename of the
program being
loaded, but can be NULL if no arguments are being passed.
The last member of argv must be a NULL
pointer.
The value of argv can't be NULL.
- envp
- A pointer to an array of character
pointers, each pointing to a string defining an environment variable.
The array is terminated with a NULL pointer.
Each pointer points to a character string of the form:
variable=value
that's used to define an environment variable.
If the value of envp is NULL, then the child
process inherits the environment of the parent process.
libc
Use the -l c option to
qcc
to link against this library.
This library is usually included automatically.
The spawn() function creates and executes a new child process, named in path.
 |
If the child process is a shell script, the first line must start with
#!, followed by the path and arguments of the shell to be run
to interpret the script. The script must also be marked as executable. |
The spawn() function is a QNX Neutrino function (based on
the POSIX 1003.1d draft standard).
The C library also includes several specialized spawn*() functions.
Their names consist of spawn followed by several letters:
| This suffix:
|
Indicates the function takes these arguments:
|
| e
|
An array of environment variables.
|
| l
|
A NULL-terminated list of arguments to the program.
|
| p
|
A relative path. If the path doesn't contain a slash, the
PATH environment variable is searched for the program.
This suffix also lets the #! construction work; see
SPAWN_CHECK_SCRIPT, below.
|
| v
|
A vector of arguments to the program. |
As shown below, these functions eventually call spawn(),
which in turn sends a message to the process manager.
To view the documentation for a function, click its name in this diagram:
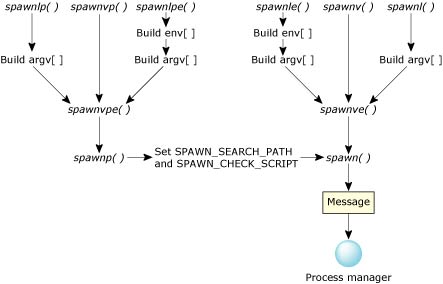
Most of the spawn*() functions do a lot of work before a message is sent to
procnto.
The child process inherits the following attributes of the parent process:
- process group ID (unless SPAWN_SETGROUP is set in inherit.flags)
- session membership
- real user ID and real group ID
- effective user ID and effective group ID
- supplementary group IDs
- priority and scheduling policy
- current working directory and root directory
- file-creation mask
- signal mask (unless SPAWN_SETSIGMASK is set in inherit.flags)
- signal actions specified as SIG_DFL
- signal actions specified as SIG_IGN (except the
ones modified by inherit.sigdefault when
SPAWN_SETSIGDEF is set in inherit.flags).
The child process has several differences from the parent process:
- Signals set to be caught by the parent process are set to the
default action (SIG_DFL).
- The child process's tms_utime, tms_stime,
tms_cutime, and tms_cstime are tracked separately
from the parent's.
- File locks set by the parent aren't inherited.
- Per-process timers created by the parent aren't inherited.
- Memory locks and mappings set by the parent aren't inherited.
The child process also has these differences from the parent process
if you haven't set the SPAWN_EXEC flag:
- The number of seconds left until a SIGALRM signal
would be generated is set to zero for the child process.
- The set of pending signals for the child process is empty.
If the child process is spawned on a remote node, the process group ID and
the session membership aren't set;
the child process is put into a new session and a new process group.
The child process can access its environment by using the
environ
global variable (found in <unistd.h>).
If the path is on a filesystem mounted with the ST_NOSUID flag set,
the effective user ID, effective group ID, saved set-user ID and saved set-group ID are unchanged for the child process.
Otherwise, if the set-user ID mode bit is set, the effective user ID of the child process is set
to the owner ID of path.
Similarly, if the set-group ID mode bit is set, the effective group ID of the child process
is set to the group ID of path.
The real user ID, real group ID and supplementary group IDs of the child process remain the same as
those of the parent process.
The effective user ID and effective group ID of the child process are saved as the saved set-user ID and
the saved set-group ID used by the
setuid().
 |
A parent/child relationship doesn't imply that the child process dies when the parent process dies. |
The inheritance structure contains at least these members:
- unsigned long flags
- Zero or more of the following bits:
- SPAWN_ALIGN_DEFAULT -- use the system's default
settings for alignment.
- SPAWN_ALIGN_FAULT -- try to always fault data
misalignment references.
- SPAWN_ALIGN_NOFAULT -- don't fault on misalignment;
attempt to fix it (this may be slow).
- SPAWN_CHECK_SCRIPT -- if path starts
with #!, spawn that binary instead, passing
path as the first argument, then the arguments after the
binary, then the original arguments.
- SPAWN_DEBUG -- debug process (this is used only
for debugging the kernel itself).
- SPAWN_EXEC -- cause the spawn to act like
exec*(): replace the calling program in memory with the
newly loaded program.
If successful, no return is made to the calling program.
- SPAWN_EXPLICIT_CPU -- set the runmask and inherit mask equal
to the runmask member of the inheritance structure. If this flag isn't set,
the child inherits the inherit mask of the calling thread.
 |
This flag was added in the QNX Neutrino Core OS 6.3.2. |
- SPAWN_EXPLICIT_SCHED -- set the scheduling policy
to the value of the policy member, and the scheduling parameters
to the value of the param member.
- SPAWN_HOLD -- hold a process for debugging
(i.e. send the SIGHOLD signal to the process before it
executes its first instruction).
- SPAWN_NOZOMBIE -- prevent the child process from
becoming a zombie on its death.
No child return or exit information will be available.
- SPAWN_SEARCH_PATH -- search the PATH
environment variable for the executable.
- SPAWN_SETGROUP -- set the child's process group to
the value in the pgroup member.
If this flag isn't set, the child process is part of the current
process group.
- SPAWN_SETND -- spawn the child process on the
node specified by the nd member.
- SPAWN_SETSID -- make the new process a session
leader.
- SPAWN_SETSIGDEF -- use the sigdefault
member to specify the child process's set of defaulted signals.
If this flag isn't specified, the child process inherits the
parent process's signal actions.
- SPAWN_SETSIGIGN -- set the handling for signals
defined in the sigignore member to SIG_IGN.
- SPAWN_SETSIGMASK -- use the sigmask
member to specify the child process's signal mask.
- SPAWN_SETSTACKMAX -- set the maximum stack size
to the value of the stack_max member.
- SPAWN_TCSETPGROUP -- start a new terminal group.
The <spawn.h> file also defines
SPAWN_ALIGN_MASK. It's a mask for the alignment flags listed
above.
- pid_t pgroup
- The child process's group if SPAWN_SETGROUP is
specified in the flags member.
If SPAWN_SETGROUP is set in inherit.flags and
inherit.pgroup is set to SPAWN_NEWPGROUP, the
child process starts a new process group with the process group ID set
to its process ID.
- int runmask
- The child process's processor affinity - the ability to associate the
process with a particular processor.
 |
This member was added in the QNX Neutrino Core OS 6.3.2. |
- sigset_t sigmask
- The child process's signal mask if you specify
SPAWN_SETSIGMASK in the flags member.
- sigset_t sigdefault
- The child process's set of defaulted signals if you specify
SPAWN_SETSIGDEF in the flags member.
- sigset_t sigignore
- The child process's set of ignored signals if you specify
SPAWN_SETSIGIGN in the flags member.
- unsigned long stack_max
- The maximum stack size for the child process, if you set
SPAWN_SETSTACKMAX in the flags member.
- int policy
- The scheduling policy for the child process, if you set
SPAWN_EXPLICIT_SCHED in the flags member.
The policy must be one of the following:
- SCHED_FIFO -- a fixed-priority scheduler in which
the highest priority ready thread runs until it blocks or is preempted
by a higher priority thread.
- SCHED_RR -- similar to SCHED_FIFO,
except that threads at the same priority level timeslice (round robin)
every 4 * the clock period (see
ClockPeriod()).
- SCHED_OTHER -- currently the same as
SCHED_RR.
- SCHED_SPORADIC -- sporadic scheduling.
- uint32_t nd
- The node descriptor of the remote node on which to spawn the child
process.
This member is used only if you set SPAWN_SETND in the
flags member.
 |
If you want to spawn() remotely, set the nd member to
the node descriptor. See the
netmgr_strtond()
function. |
- struct sched_param param
- Scheduling parameters for the child process, if you set
SPAWN_EXPLICIT_SCHED in the flags member.
For more information, see the documentation for
sched_param.
The process ID of the child process, or -1 if an error occurs
(errno is set).
 |
If you set SPAWN_EXEC in the flags member of
the inheritence structure, spawn() doesn't return,
unless an error occurred. |
- E2BIG
- The number of bytes used by the argument list and environment list of the new child process
is greater than ARG_MAX bytes.
- EACCESS
- Search permission is denied for a directory listed in the path prefix
of the new child process or the child process's file doesn't have the execute
bit set or path's filesystem was mounted with the ST_NOEXEC flag.
- EAGAIN
- Insufficient resources available to create the child process.
- EBADF
- An entry in fd_map refers to an invalid file descriptor, or
an error occurred duplicating open file descriptors to the new process.
- EFAULT
- One of the buffers specified in the function call is invalid.
- ELOOP
- Too many levels of symbolic links or prefixes.
- EMFILE
- Insufficient resources available to load the new executable
image or to remap file descriptors in the child process.
- ENAMETOOLONG
- The length of path exceeds PATH_MAX or a
pathname component is longer than NAME_MAX.
- ENOENT
- The file identified by the path argument is empty,
or one or more components of the pathname of the child process don't exist.
- ENOEXEC
- The child process's file has the correct permissions, but isn't in the correct format for an executable.
(This error doesn't occur if SPAWN_CHECK_SCRIPT is
set in the flags member of the inheritance
structure.)
- ENOMEM
- Insufficient memory available to create the child process.
- ENOSYS
- The spawn() function isn't implemented for the filesystem specified in path.
- ENOTDIR
- A component of the path prefix of the child process isn't a directory.
QNX Neutrino
| Safety: | |
|---|
| Cancellation point |
No |
| Interrupt handler |
No |
| Signal handler |
Yes |
| Thread |
Yes |
execl(),
execle(),
execlp(),
execlpe(),
execv(),
execve(),
execvp(),
execvpe(),
getenv(),
netmgr_strtond(),
putenv(),
sched_param,
setenv(),
sigaddset(),
sigdelset(),
sigemptyset(),
sigfillset(),
spawnl(),
spawnle(),
spawnlp(),
spawnlpe(),
spawnp(),
spawnv(),
spawnve(),
spawnvp(),
spawnvpe(),
wait(),
waitpid()
![[Previous]](../prev.gif)
![[Contents]](../contents.gif)
![[Index]](../keyword_index.gif)
![[Next]](../next.gif)
![[Previous]](../prev.gif)
![[Contents]](../contents.gif)
![[Index]](../keyword_index.gif)
![[Next]](../next.gif)








![[Previous]](../prev.gif)
![[Contents]](../contents.gif)
![[Index]](../keyword_index.gif)
![[Next]](../next.gif)