![[Previous]](prev.gif) |
![[Contents]](contents.gif) |
![[Index]](keyword_index.gif) |
![[Next]](next.gif) |
![[Previous]](prev.gif) |
![[Contents]](contents.gif) |
![[Index]](keyword_index.gif) |
![[Next]](next.gif) |
 |
This version of this document is no longer maintained. For the latest documentation, see http://www.qnx.com/developers/docs. |
You can select a topic from this diagram:
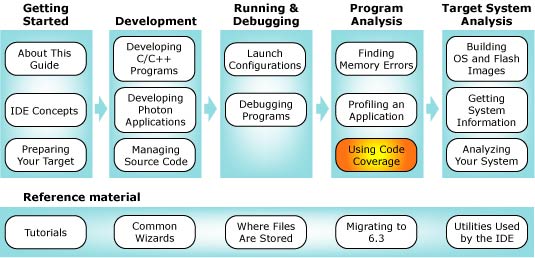
Use the Code Coverage tool to help test your code.
Code coverage is a way to measure how much code a particular process has executed during a test or benchmark. Using code-coverage analysis, you can then create additional test cases to increase coverage and determine a quantitative measure of code coverage, which is an indirect measure of the quality of your software (or better, a direct measure of the quality of your tests).
Several types of metrics are commonly used in commercial code-coverage tools, ranging from simple line or block coverage (i.e. "this statement was executed") to condition-decision coverage (i.e. "all terms in this Boolean expression are exercised"). A given tool usually provides a combination of types.
The coverage tool in the IDE is a visual font end to the gcov metrics produced by the gcc compiler. These coverage metrics are essentially basic block coverage and branch coverage.
The IDE presents these metrics as line coverage, showing which lines are fully covered, partially covered, and not covered at all. The IDE also presents percentages of coverage in terms of the actual code covered (i.e. not just lines).
Block coverage, sometimes known as line coverage, describes whether a block of code, defined as not having any branch point within (i.e. the path of execution will enter from the beginning and exit at the end.) is executed or not.
By tracking the number of times the block of code has been executed, the IDE can determine the total coverage of a particular file or function. The tool also uses this information to show line coverage by analyzing the blocks on each line and determining the level of coverage of each.
Branch coverage can track the path of execution taken between blocks of code. Although this metric is produced by the gcc compiler, currently the IDE doesn't provide this information.
The IDE's code coverage tool works in conjunction with the compiler (gcc), the QNX C library (libc), and optionally the remote target agent (qconn). When code coverage is enabled for an application, the compiler will instrument the code so that at run time, each branch execution to a basic block is counted. During the build, the IDE produces data files in order to recreate the program's flow graph and to provide line locations of each block.
 |
Since the IDE creates secondary data files at compilation
time, you must be careful when building your programs in a
multi-targeted build environment such as QNX Neutrino.
You must either:
Note also that the compiler's optimizations could produce unexpected results, so you should perform coverage tests on a non-optimized, debug-enabled build. |
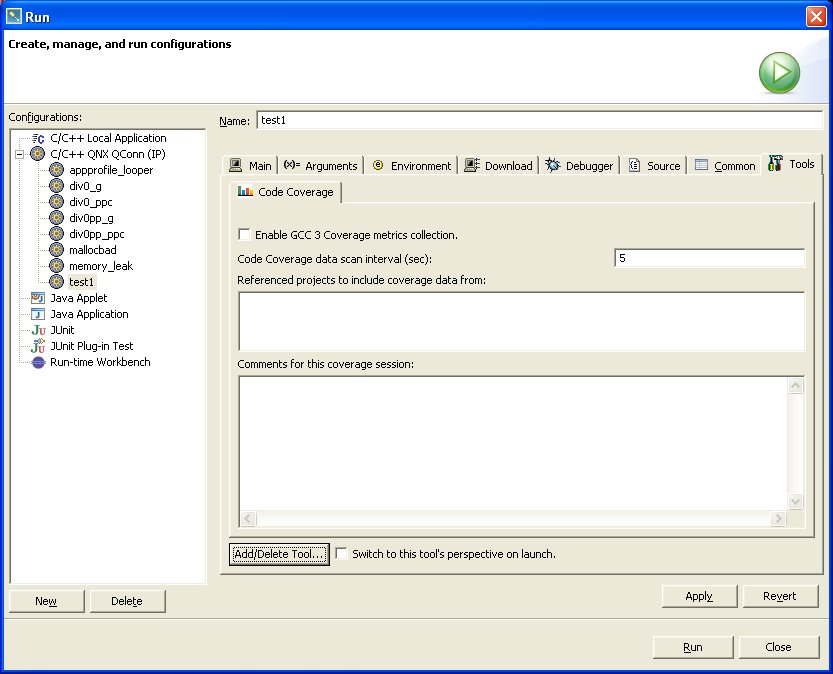
When you build a program with the Build with Code Coverage build option enabled and then launch it using a C/C++ QNX Qconn (IP) launch configuration, the instrumented code linked into the process will connect to qconn, allowing the coverage data to be read from the process's data space.
But if you launch a coverage-built process with coverage disabled in the launch configuration, this will cause the process to write the coverage information to a data file (.da) at run time, rather than read it from the process's data space.
 |
You should use data files only if you're running the local launch configuration on a QNX Neutrino self-hosted development system. Note that the data can later be imported into the IDE code coverage tool. |
Once a coverage session has begun, you can immediately view the data. The QNX Code Coverage perspective contains a Code Coverage Sessions view that lists previous as well as currently active sessions. You can explore each session and browse the corresponding source files that have received coverage data.
To build executables with code coverage enabled:
 |
If the IDE is set to build more than one variant, an error is displayed and the OK button is disabled. |
If you're using your own custom build environment, rather than QNX makefiles, you'll have to manually pass the coverage option to the compiler.
To enable code coverage for non-QNX projects
-fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage
If your using qcc, compile with:
-Wc,-fprofile-arcs -Wc,-ftest-coverage
For example, your makefile might look something like this:
objects:=Profile.o main.o
CC:=qcc -Vgcc_ntox86
CFLAGS:=-g -Wc,-ftest-coverage -Wc,-fprofile-arcs -I. -I../proflibCPP-std
LDFLAGS:=-p -g -L../proflibCPP-std -lProfLib -lcpp
all: profileCPP-std
clean:
-rm $(objects) profileCPP-std *.bb *.bbg
profileCPP-std: $(objects)
$(CC) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
To start a program and measure the code coverage:
The Code Coverage Sessions view lets you control and display multiple code-coverage sessions:
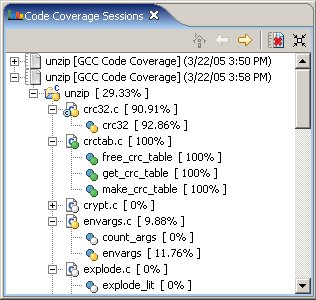
The view displays the following as a hierarchical tree for each session:
| Session item | Description | Possible icons |
|---|---|---|
| Code coverage session | Launch configuration name, coverage tool, and start time (e.g. ccov102_factor [GCC Code Coverage] (7/2/03 2:48 PM)) | |
| Project | Project name and amount of coverage (e.g. ccov102_factor [ 86.67% ]) | |
| File | Filename and amount of coverage (e.g. ccov102_factor.c [ 86.67% ]) | |
| Function | Function name and amount of coverage (e.g. main [ 100% ]) |
The IDE uses several icons in this view:
| Icon | Meaning |
|---|---|
| No coverage | |
| Partial coverage | |
| |
Full (100%) coverage |
| Missing or out-of-date source file |
The IDE also adds a coverage markup icon (![]() ) to indicate source markup in the editor.
(See the "Examining data line-by-line" section, below.)
) to indicate source markup in the editor.
(See the "Examining data line-by-line" section, below.)
To reduce the size of
the hierarchical tree, click the Collapse All
(![]() ) button.
) button.
To combine several sessions:
The IDE can display the line-by-line coverage information
for your source code. In the left margin, the editor
displays a "covered" icon (![]() ) beside
each line of source. In the right margin, the editor
displays a summary of the coverage by showing green sections for
fully-covered code, yellow for partial coverage, and red for no coverage:
) beside
each line of source. In the right margin, the editor
displays a summary of the coverage by showing green sections for
fully-covered code, yellow for partial coverage, and red for no coverage:
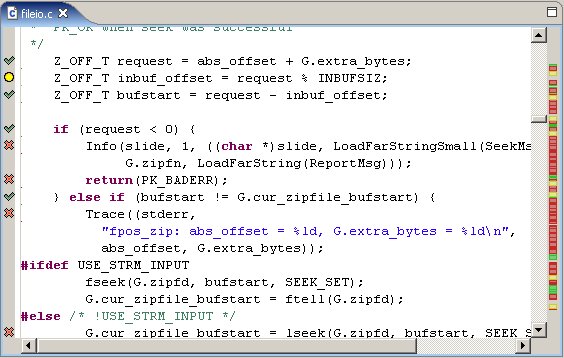
To open a file in the QNX Code Coverage perspective:
 |
In the Code Coverage Sessions view, expand a session and double-click a file or function. |
To display coverage information from a particular session:
 |
In the Code Coverage Sessions view, right-click a session
and select Coverage Markup, then select one of the
following:
The selected icon appears beside the corresponding source in
the C/C++ editor. In the Code Coverage Sessions view, a
coverage marker ( |
To automatically show coverage information when opening a file:
To remove all coverage markers:
 |
In the Code Coverage Sessions view's title bar, click the
Remove All Coverage Markers button ( |
The Code Coverage Report view provides a summary (in XML) of your session. The view lets you drill down into your project and see the coverage for individual files and functions:
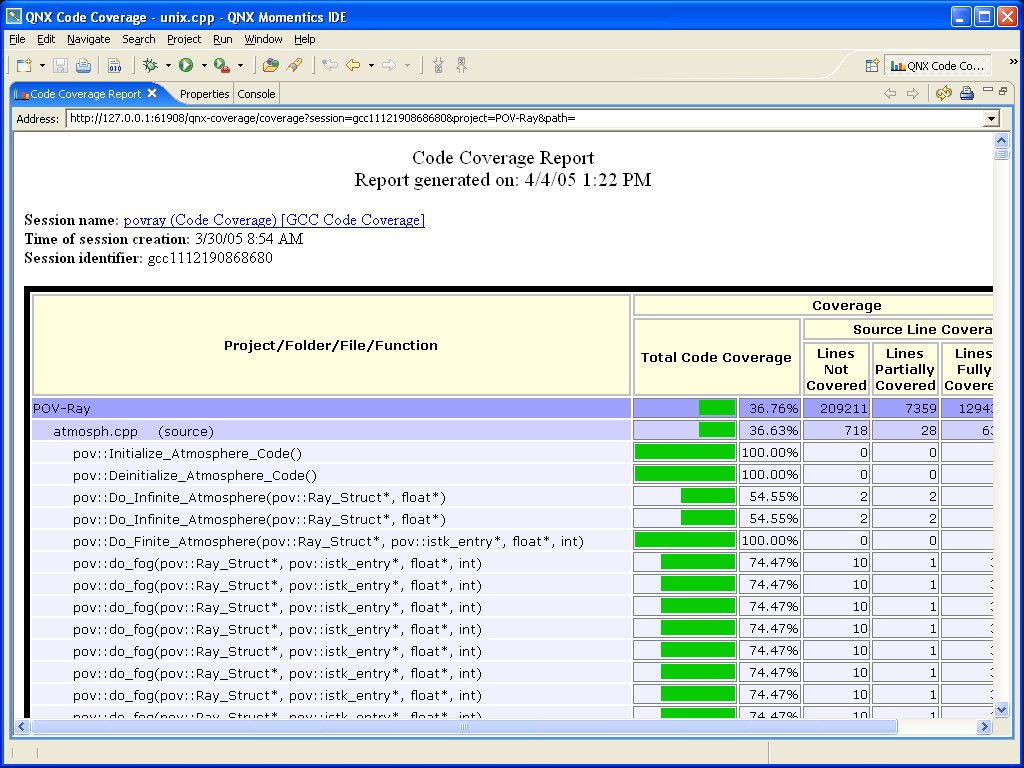
To generate a report, simply right-click a coverage session and select Generate Report.
By default, the IDE displays reports in the Code Coverage Report view, but you can also have the IDE display reports in an external browser. Using an external browser lets you compare several reports simultaneously.
To toggle between viewing reports in the Code Coverage Report view and in an external browser:
To print a report:
 |
In the Code Coverage Report view's title bar, click the
Print button ( |
To save a report:
You can also refresh the report:
 |
In the Code Coverage Report view's title bar, click the
Refresh button ( |
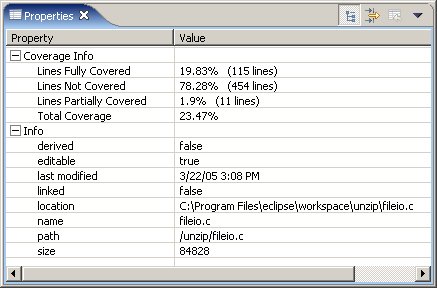
The Properties view displays a summary of the code coverage for a project, file, or function you've selected in the Code Coverage Sessions view.
The Properties view tells you how many lines were covered, not covered, and so on:
![[Previous]](prev.gif) |
![[Contents]](contents.gif) |
![[Index]](keyword_index.gif) |
![[Next]](next.gif) |